UDS Knowledge Base¶
If you are not an UDS expert, this part of documentation is created for you. It is meant to provide a technical support for every user of UDS package so you can better understand the code, but also UDS protocol itself.
UDS OSI Model¶
OSI Layer |
ISO Standards |
Functionalities |
Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
Layer 7 Application |
Common:
CAN specific:
FlexRay specific:
Ethernet specific:
K-Line specific:
LIN specific:
|
Diagnostic message:
|
To be extended in milestones: |
Layer 6 Presentation |
Common:
Unique per system:
|
|
To be implemented in milestones: |
Layer 5 Session |
Common:
|
|
To be implemented in milestones: |
Layer 4 Transport |
CAN specific:
FlexRay specific:
Ethernet specific:
LIN specific:
|
UDS packets:
UDS communication:
|
|
Layer 3 Network |
|||
Layer 2 Data |
CAN specific:
FlexRay specific:
Ethernet specific:
K-Line specific:
LIN specific:
|
Bus handling:
|
External python packages for bus handling: |
Layer 1 Physical |
Client¶
TODO DURING CLIENT EPIC
Server¶
TODO DURING SERVER EPIC
Diagnostic Message¶
If we only consider the top layer of OSI Model (layer 7 - Application), then the messages that are exchanged by clients and servers during UDS communication are called ‘Application Protocol Data Units’ (A_PDU), ‘diagnostic messages’ or ‘UDS messages’ in this documentation.
- There are two types of diagnostic messages:
diagnostic request - a message transmitted by a client
diagnostic response - a message transmitted by a server
UDS communication is always initiated by a client who sends a diagnostic request to a network that it is connected to. The client might not be directly connected to a desired recipient(s) of the request, therefore some servers might be forced to act as gateways and transmit the request to another network(s) to which they are connected. Server decision (whether to redirect the request to another vehicle sub-network or not) depends on a target(s) of the request i.e. server shall transmit the request in the sub-network if at least on ECU in this sub-network is the target of the request.
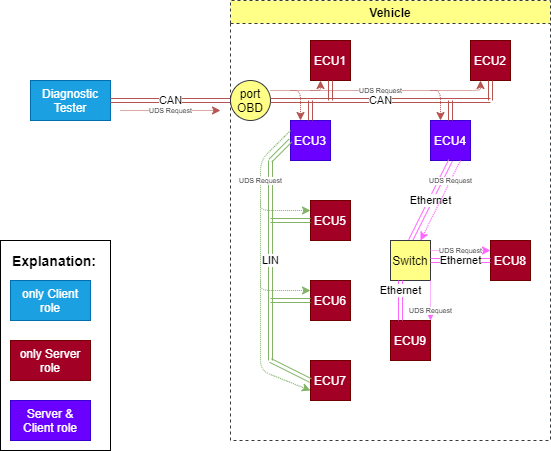
Diagnostic request routing in example vehicle networks.¶
In this example all ECUs in the vehicle are the targets of the request - functionally addressed request was sent.
Each server which was the recipient of the request, might decide to send a response back to the nearest client (the one which transmitted the request in this sub-network). Then, the client shall act as the gateway again and redirect the response back until it reaches the request message originator (Diagnostic Tester).
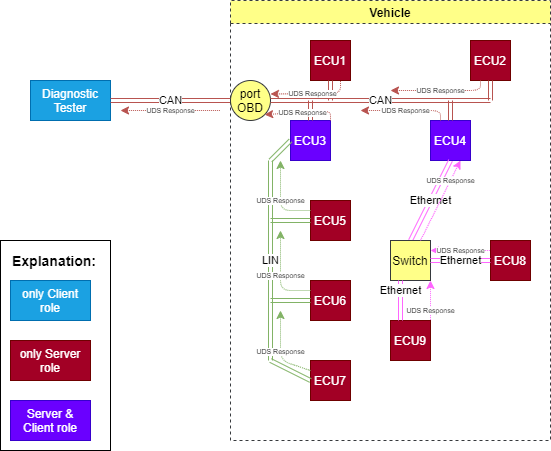
Diagnostic responses routing in example vehicle networks.¶
In this example all ECUs in the vehicle responds to the request.
Diagnostic Request¶
Diagnostic request is a diagnostic message that was transmitted by a client and targets a server or group of servers. Diagnostic request can be identified by its Service Identifier (SID) value.
Diagnostic Response¶
Diagnostic response is a diagnostic message that was transmitted by a server and targets a client. Diagnostic response can be identified by its Service Identifier (SID) value.
- UDS describes two formats of diagnostic responses:
Positive Response Message¶
If a server responds with positive response message, it means that the server received the corresponding request message and executed actions requested by a client.
Byte |
Description |
Value |
|---|---|---|
1 |
Response SID |
SID + 0x40 |
2 |
data-parameter#1 |
XX |
… |
… |
… |
n |
data-parameter#n |
XX |
- Where:
SID - Service Identifier value that was received in the request message to which the server responded
XX - any byte value
Negative Response Message¶
If a server responds with negative response message, it means that the server for some reason the server could not execute actions requested by a client.
Byte |
Description |
Value |
|---|---|---|
1 |
Negative Response SID |
0x7F |
2 |
Request SID |
SID |
3 |
NRC |
XX |
- Where:
SID - Service Identifier value that was received in the request message to which the server responded
NRC - Negative Response Code value that identified the reason for negative response
Service Identifier¶
Service Identifier (SID) is one byte integer located in the first byte of Application Data (A_Data) in the diagnostic message. SID determines whether the message is diagnostic request or diagnostic response. General purpose (application) and format of diagnostic message is also by determined by SID value.
- List of all Service Identifier (SID) values and their application:
0x00 - not applicable, reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x01-0x0F - ISO 15031-5/SAE J1979 specific services
0x10 - DiagnosticSessionControl service request
0x11 - ECUReset service request
0x12-0x13 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x14 - ClearDiagnosticInformation service request
0x15-0x18 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x19 - ReadDTCInformation service request
0x1A-0x21 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x22 - ReadDataByIdentifier service request
0x23 - ReadMemoryByAddress service request
0x24 - ReadScalingDataByIdentifier service request
0x25-0x26 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x27 - SecurityAccess service request
0x28 - CommunicationControl service request
0x29 - Authentication service request
0x2A - ReadDataByPeriodicIdentifier service request
0x2B - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x2C - DynamicallyDefineDataIdentifier service request
0x2D - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x2E - WriteDataByIdentifier service request
0x2F - InputOutputControlByIdentifier service request
0x30 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x31 - RoutineControl service request
0x32-0x33 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x34 - RequestDownload service request
0x35 - RequestUpload service request
0x36 - TransferData service request
0x37 - RequestTransferExit service request
0x38 - RequestFileTransfer service request
0x39-0x3C - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x3D - WriteMemoryByAddress service request
0x3E - TesterPresent service request
0x3F - not applicable, reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x40 - not applicable, reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x41-0x4F - ISO 15031-5/SAE J1979 specific services
0x50 - positive response to DiagnosticSessionControl service
0x51 - positive response to ECUReset service
0x52-0x53 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x54 - positive response to ClearDiagnosticInformation service
0x55-0x58 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x59 - positive response to ReadDTCInformation service
0x5A-0x61 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x62 - positive response to ReadDataByIdentifier service
0x63 - positive response to ReadMemoryByAddress service
0x64 - positive response to ReadScalingDataByIdentifier service
0x65-0x66 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x67 - positive response to SecurityAccess service
0x68 - positive response to CommunicationControl service
0x69 - positive response to Authentication service
0x6A - positive response to ReadDataByPeriodicIdentifier service
0x6B - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x6C - positive response to DynamicallyDefineDataIdentifier service
0x6D - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x6E - positive response to WriteDataByIdentifier service
0x6F - positive response to InputOutputControlByIdentifier service
0x70 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x71 - positive response to RoutineControl service
0x72-0x73 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x74 - positive response to RequestDownload service
0x75 - positive response to RequestUpload service
0x76 - positive response to TransferData service
0x77 - positive response to RequestTransferExit service
0x78 - positive response to RequestFileTransfer service
0x79-0x7C - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x7D - positive response to WriteMemoryByAddress service
0x7E - positive response to TesterPresent service
0x7F - negative response service identifier
0x80-0x82 - not applicable, reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x83 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x84 - SecuredDataTransmission service request
0x85 - ControlDTCSetting service request
0x86 - ResponseOnEvent service request
0x87 - LinkControl service request
0x88 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0x89-0xB9 - not applicable, reserved by ISO 14229-1
0xBA-0xBE - system supplier specific service requests
0xBF-0xC2 - not applicable, reserved by ISO 14229-1
0xC3 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0xC4 - positive response to SecuredDataTransmission service
0xC5 - positive response to ControlDTCSetting service
0xC6 - positive response to ResponseOnEvent service
0xC7 - positive response to LinkControl service
0xC8 - reserved by ISO 14229-1
0xC9-0xF9 - not applicable, reserved by ISO 14229-1
0xFA-0xFE - positive responses to system supplier specific requests
0xFF - not applicable, reserved by ISO 14229-1
DiagnosticSessionControl¶
DiagnosticSessionControl service is used to change diagnostic sessions in the server(s). In each diagnostic session a different set of diagnostic services (and/or functionalities) is enabled in the server. Server shall always be in exactly one diagnostic session.
ECUReset¶
ECUReset service is used by the client to request a server reset.
ClearDiagnosticInformation¶
ClearDiagnosticInformation service is used by the client to clear all diagnostic information (DTC and related data) in one or multiple servers’ memory.
ReadDTCInformation¶
ReadDTCInformation service allows the client to read from any server or group of servers within a vehicle, current information about all Diagnostic Trouble Codes. This could be a status of reported Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC), number of currently active DTCs or any other information returned by supported ReadDTCInformation SubFunctions.
ReadDataByIdentifier¶
ReadDataByIdentifier service allows the client to request data record values from the server identifier by one or more DataIdentifiers (DIDs).
ReadMemoryByAddress¶
ReadMemoryByAddress service allows the client to request server’s memory data stored under provided memory address.
ReadScalingDataByIdentifier¶
ReadScalingDataByIdentifier service allows the client to request from the server a scaling data record identified by a DataIdentifier (DID). The scaling data contains information such as data record type (e.g. ASCII, signed float), formula and its coefficients used for value calculation, units, etc.
SecurityAccess¶
SecurityAccess service allows the client to unlock functions/services with restricted access.
CommunicationControl¶
CommunicationControl service allows the client to switch on/off the transmission and/or the reception of certain messages on a server(s).
Authentication¶
Authentication service provides a means for the client to prove its identity, allowing it to access data and/or diagnostic services, which have restricted access for, for example security, emissions, or safety reasons.
ReadDataByPeriodicIdentifier¶
ReadDataByPeriodicIdentifier service allows the client to request the periodic transmission of data record values from the server identified by one or more periodicDataIdentifiers.
DynamicallyDefineDataIdentifier¶
DynamicallyDefineDataIdentifier service allows the client to dynamically define in a server a DataIdentifier (DID) that can be read via the ReadDataByIdentifier service at a later time.
WriteDataByIdentifier¶
WriteDataByIdentifier service allows the client to write information into the server at an internal location specified by the provided DataIdentifier (DID).
InputOutputControlByIdentifier¶
InputOutputControlByIdentifier service allows the client to substitute a value for an input signal, internal server function and/or force control to a value for an output (actuator) of an electronic system.
RoutineControl¶
RoutineControl service allows the client to execute a defined sequence of steps to obtain any relevant result. There is a lot of flexibility with this service, but typical usage may include functionality such as erasing memory, resetting or learning adaptive data, running a self-test, overriding the normal server control strategy.
RequestDownload¶
RequestDownload service allows the client to initiate a data transfer from the client to the server (download).
RequestUpload¶
RequestUpload service allows the client to initiate a data transfer from the server to the client (upload).
TransferData¶
TransferData service is used by the client to transfer data either from the client to the server (download) or from the server to the client (upload).
RequestTransferExit¶
RequestTransferExit service is used by the client to terminate a data transfer between the client and server.
RequestFileTransfer¶
RequestFileTransfer service allows the client to initiate a file data transfer either from the server to the client (upload) or from the server to the client (upload).
WriteMemoryByAddress¶
WriteMemoryByAddress service allows the client to write information into server’s memory data under provided memory address.
TesterPresent¶
TesterPresent service is used by the client to indicate to a server(s) that the client is still connected to a vehicle and certain diagnostic services and/or communication that have been previously activated are to remain active.
SecuredDataTransmission¶
SecuredDataTransmission service is applicable if a client intends to use diagnostic services defined in this document in a secured mode. It may also be used to transmit external data, which conform to some other application protocol, in a secured mode between a client and a server. A secured mode in this context means that the data transmitted is protected by cryptographic methods.
ControlDTCSetting¶
ControlDTCSetting service allows the client to stop or resume the updating of DTC status bits in the server(s) memory.
ResponseOnEvent¶
ResponseOnEvent service allows the client to request from the server to start ot stop transmission of responses on a specified event.
LinkControl¶
LinkControl service allows the client to control the communication between the client and the server(s) in order to gain bus bandwidth for diagnostic purposes (e.g. programming).
Negative Response Code¶
Negative Response Code (NRC) is one byte value which contains information why a server is not sending a positive response message.
- List of NRC values:
0x00 - positiveResponse - This NRC shall not be used in a negative response message. This positiveResponse parameter value is reserved for server internal implementation.
0x00-0x0F - ISO Reserved - This range of values is reserved for future definition by ISO 14229 Standard.
0x10 - generalReject - This NRC indicates that the requested action has been rejected by the server.
0x11 - serviceNotSupported - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server does not support the requested service.
0x12 - SubFunctionNotSupported - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server does not support the service specific parameters of the request message.
0x13 - incorrectMessageLengthOrInvalidFormat - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the length of the received request message does not match the prescribed length for the specified service or the format of the parameters do not match the prescribed format for the specified service.
0x14 - responseTooLong - This NRC shall be reported by the server if the response to be generated exceeds the maximum number of bytes available by the underlying network layer. This could occur if the response message exceeds the maximum size allowed by the underlying transport protocol or if the response message exceeds the server buffer size allocated for that purpose.
0x15-0x20 - ISO Reserved - This range of values is reserved for future definition by ISO 14229 Standard.
0x21 - busyRepeatRequest - This NRC indicates that the server is temporarily too busy to perform the requested operation. In this circumstance the client shall perform repetition of the “identical request message” or “another request message”. The repetition of the request shall be delayed by a time specified in the respective implementation documents.
0x22 - conditionsNotCorrect - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite conditions are not met.
0x23 - ISO Reserved - This value is reserved for future definition by ISO 14229 Standard.
0x24 - requestSequenceError - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server expects a different sequence of request messages or message as sent by the client. This may occur when sequence sensitive requests are issued in the wrong order.
0x25 - noResponseFromSubnetComponent - This NRC indicates that the server has received the request but the requested action could not be performed by the server as a subnet component which is necessary to supply the requested information did not respond within the specified time.
0x26 - FailurePreventsExecutionOfRequestedAction - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because a failure condition, identified by a DTC (with at least one DTC status bit for TestFailed, Pending, Confirmed or TestFailedSinceLastClear set to 1), has occurred and that this failure condition prevents the server from performing the requested action.
0x27-0x30 - ISO Reserved - This range of values is reserved for future definition by ISO 14229 Standard.
0x31 - requestOutOfRange - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server has detected that the request message contains a parameter which attempts to substitute a value beyond its range of authority (e.g. attempting to substitute a data byte of 111 when the data is only defined to 100), or which attempts to access a DataIdentifier/RoutineIdentifer that is not supported or not supported in active session.
0x32 - ISO Reserved - This value is reserved for future definition by ISO 14229 Standard.
0x33 - securityAccessDenied - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server’s security strategy has not been satisfied by the client.
0x34 - authenticationRequired - This NRC indicates that the requested service will not be taken because the client has insufficient rights based on its Authentication state.
0x35 - invalidKey - This NRC indicates that the server has not given security access because the key sent by the client did not match with the key in the server’s memory. This counts as an attempt to gain security.
0x36 - exceedNumberOfAttempts - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the client has unsuccessfully attempted to gain security access more times than the server’s security strategy will allow.
0x37 - requiredTimeDelayNotExpired - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the client’s latest attempt to gain security access was initiated before the server’s required timeout period had elapsed.
0x38 - secureDataTransmissionRequired - This NRC indicates that the requested service will not be taken because the requested action is required to be sent using a secured communication channel.
0x39 - secureDataTransmissionNotAllowed - This NRC indicates that this message was received using the SecuredDataTransmission (SID 0x84) service. However, the requested action is not allowed to be sent using the SecuredDataTransmission (0x84) service.
0x3A - secureDataVerificationFailed - This NRC indicates that the message failed in the security sub-layer.
0x3B-0x4F - ISO Reserved - This range of values is reserved for future definition by ISO 14229 Standard.
0x50 - Certificate verification failed, Invalid Time Period - Date and time of the server does not match the validity period of the Certificate.
0x51 - Certificate verification failed, Invalid Signature - Signature of the Certificate could not be verified.
0x52 - Certificate verification failed, Invalid Chain of Trust - Certificate could not be verified against stored information about the issuing authority.
0x53 - Certificate verification failed, Invalid Type - Certificate does not match the current requested use case.
0x54 - Certificate verification failed, Invalid Format - Certificate could not be evaluated because the format requirement has not been met.
0x55 - Certificate verification failed, Invalid Content - Certificate could not be verified because the content does not match.
0x56 - Certificate verification failed, Invalid Scope - The scope of the Certificate does not match the contents of the server.
0x57 - Certificate verification failed, Invalid Certificate (revoked) - Certificate received from client is invalid, because the server has revoked access for some reason.
0x58 - Ownership verification failed - Delivered Ownership does not match the provided challenge or could not verified with the own private key.
0x59 - Challenge calculation failed - The challenge could not be calculated on the server side.
0x5A - Setting Access Rights failed - The server could not set the access rights.
0x5B - Session key creation/derivation failed - The server could not create or derive a session key.
0x5C - Configuration data usage failed - The server could not work with the provided configuration data.
0x5D - DeAuthentication failed - DeAuthentication was not successful, server could still be unprotected.
0x5E-0x6F - ISO Reserved - This range of values is reserved for future definition by ISO 14229 Standard.
0x70 - uploadDownloadNotAccepted - This NRC indicates that an attempt to upload/download to a server’s memory cannot be accomplished due to some fault conditions.
0x71 - transferDataSuspended - This NRC indicates that a data transfer operation was halted due to some fault. The active transferData sequence shall be aborted.
0x72 - generalProgrammingFailure - This NRC indicates that the server detected an error when erasing or programming a memory location in the permanent memory device (e.g. Flash Memory).
0x73 - wrongBlockSequenceCounter - This NRC indicates that the server detected an error in the sequence of blockSequenceCounter values. Note that the repetition of a TransferData request message with a blockSequenceCounter equal to the one included in the previous TransferData request message shall be accepted by the server.
0x74-0x77 - ISO Reserved - This range of values is reserved for future definition by ISO 14229 Standard.
0x78 - requestCorrectlyReceived-ResponsePending - This NRC indicates that the request message was received correctly, and that all parameters in the request message were valid (these checks can be delayed until after sending this NRC if executing the boot software), but the action to be performed is not yet completed and the server is not yet ready to receive another request. As soon as the requested service has been completed, the server shall send a positive response message or negative response message with a response code different from this.
0x79-0x7D - ISO Reserved - This range of values is reserved for future definition by ISO 14229 Standard.
0x7E - SubFunctionNotSupportedInActiveSession - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server does not support the requested SubFunction in the session currently active. This NRC shall only be used when the requested SubFunction is known to be supported in another session, otherwise response code SubFunctionNotSupported shall be used.
0x7F - serviceNotSupportedInActiveSession - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server does not support the requested service in the session currently active. This NRC shall only be used when the requested service is known to be supported in another session, otherwise response code serviceNotSupported shall be used.
0x80 - ISO Reserved - This value is reserved for future definition by ISO 14229 Standard.
0x81 - rpmTooHigh - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for RPM is not met (current RPM is above a preprogrammed maximum threshold).
0x82 - rpmTooLow - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for RPM is not met (current RPM is below a preprogrammed minimum threshold).
0x83 - engineIsRunning - This NRC is required for those actuator tests which cannot be actuated while the Engine is running. This is different from RPM too high negative response, and shall be allowed.
0x84 - engineIsNotRunning - This NRC is required for those actuator tests which cannot be actuated unless the Engine is running. This is different from RPM too low negative response, and shall be allowed.
0x85 - engineRunTimeTooLow - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for engine run time is not met (current engine run time is below a preprogrammed limit).
0x86 - temperatureTooHigh - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for temperature is not met (current temperature is above a preprogrammed maximum threshold).
0x87 - temperatureTooLow - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for temperature is not met (current temperature is below a preprogrammed minimum threshold).
0x88 - vehicleSpeedTooHigh - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for vehicle speed is not met (current VS is above a preprogrammed maximum threshold).
0x89 - vehicleSpeedTooLow - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for vehicle speed is not met (current VS is below a preprogrammed minimum threshold).
0x8A - throttle/PedalTooHigh - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for throttle/pedal position is not met (current throttle/pedal position is above a preprogrammed maximum threshold).
0x8B - throttle/PedalTooLow - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for throttle/pedal position is not met (current throttle/pedal position is below a preprogrammed minimum threshold).
0x8C - transmissionRangeNotInNeutral - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for being in neutral is not met (current transmission range is not in neutral).
0x8D - transmissionRangeNotInGear - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for being in gear is not met (current transmission range is not in gear).
0x8E - ISO Reserved - This value is reserved for future definition by ISO 14229 Standard.
0x8F - brakeSwitch(es)NotClosed (Brake Pedal not pressed or not applied) - This NRC indicates that for safety reasons, this is required for certain tests before it begins, and shall be maintained for the entire duration of the test.
0x90 - shifterLeverNotInPark - This NRC indicates that for safety reasons, this is required for certain tests before it begins, and shall be maintained for the entire duration of the test.
0x91 - torqueConverterClutchLocked - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for torque converter clutch is not met (current torque converter clutch status above a preprogrammed limit or locked).
0x92 - voltageTooHigh - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for voltage at the primary pin of the server (ECU) is not met (current voltage is above a preprogrammed maximum threshold).
0x93 - voltageTooLow - This NRC indicates that the requested action will not be taken because the server prerequisite condition for voltage at the primary pin of the server (ECU) is not met (current voltage is below a preprogrammed maximum threshold).
0x94 - ResourceTemporarilyNotAvailable - This NRC indicates that the server has received the request but the requested action could not be performed by the server because an application which is necessary to supply the requested information is temporality not available. This NRC is in general supported by each diagnostic service, as not otherwise stated in the data link specific implementation document, therefore it is not listed in the list of applicable response codes of the diagnostic services.
0x95-0xEF - reservedForSpecificConditionsNotCorrect - This range of values is reserved for future definition condition not correct scenarios by ISO 14229 Standard.
0xF0-0xFE - vehicleManufacturerSpecificConditionsNotCorrect - This range of values is reserved for vehicle manufacturer specific condition not correct scenarios.
0xFF - ISO Reserved - This value is reserved for future definition by ISO 14229 Standard.
Addressing¶
Addressing determines model of UDS communication.
- We distinguish following addressing types:
Physical¶
Physical addressing is used to send a dedicated message to a certain server (ECU). When physically addressed messages are sent, the direct (point-to-point) communication between the client and the server takes place. The server shall respond to physically addressed request unless the request contains an information that response is not required (further explained in`response behaviour to physically addressed request`_ chapter).
NOTE: You do not need a direct physical connection between the client and the server to have physically addressed communication as all messages shall be routed to a target of each message.
Response behaviour to physically addressed request¶
Expected server behaviour in case of receiving physically addressed request message with SubFunction parameter:
Client request |
Server capability |
Server response |
Comment |
||||
Addressing |
SPRMIB |
SID supported |
SF supported |
DataParam supported |
Message |
NRC |
|
physical |
False (bit = 0) |
YES |
YES |
At least 1 |
Positive Response |
— |
Server supports the requests and sends positive response. |
At least 1 |
Negative Response |
NRC = XX |
Server sends negative response because an error occurred processing the data parameters of request message. |
||||
None |
NRC = ROOR |
Servers sends negative response with NRC 0x31. |
|||||
NO |
— |
— |
NRC = SNS or SNSIAS |
Servers sends negative response with NRC 0x11 or 0x7F. |
|||
YES |
NO |
— |
NRC = SFNS or SFNSIAS |
Servers sends negative response with NRC 0x12 or 0x7E. |
|||
True (bit = 1) |
YES |
YES |
At least 1 |
No Response |
— |
Server does not send a response. |
|
At least 1 |
Negative Response |
NRC = XX |
Server sends negative response because an error occurred processing the data parameters of request message. |
||||
None |
NRC = ROOR |
Servers sends negative response with NRC 0x31. |
|||||
NO |
— |
— |
NRC = SNS or SNSIAS |
Servers sends negative response with NRC 0x11 or 0x7F. |
|||
YES |
NO |
— |
NRC = SFNS or SFNSIAS |
Servers sends negative response with NRC 0x12 or 0x7E. |
|||
Expected server behaviour in case of receiving physically addressed request message without SubFunction parameter:
Client request |
Server capability |
Server response |
Comment |
||
Addressing |
SID supported |
DataParam supported |
Message |
NRC |
|
physical |
YES |
All |
Positive Response |
— |
Server supports the requests and sends positive response. |
At least 1 |
— |
Server supports the requests and sends positive response. |
|||
At least 1 |
Negative Response |
NRC = XX |
Server sends negative response because an error occurred processing the data parameters of request message. |
||
None |
NRC = ROOR |
Servers sends negative response with NRC 0x31. |
|||
NO |
— |
NRC = SNS or SNSIAS |
Servers sends negative response with NRC 0x11 or 0x7F |
||
- Where:
SPRMIB - flag informing whether Suppress Positive Response Message Indication Bit is set in the received request message
SID supported - flag informing whether Service Identifier in the received request message is supported by the server
SF supported - flag informing whether SubFunction in the received request message is supported by the server
DataParam supported - information whether values of data parameters (e.g. DIDs, RIDs, DTCStatusMask) in the received request message are supported by the server
NRC - Negative Response Code
ROOR - NRC 0x31 (requestOutOfRange)
SNS - NRC 0x11 (serviceNotSupported)
SNSIAS - NRC 0x7F (serviceNotSupportedInActiveSession)
SFNS - NRC 0x12 (SubFunctionNotSupported)
SFNSIAS - NRC 0x7E (SubFunctionNotSupportedInActiveSession)
XX - NRC code that is supported by the server and suitable to the current situation (e.g. NRC 0x21 busyRepeatRequest if server is currently overloaded and cannot process next request message)
Functional¶
Functional addressing is used to send messages to multiple servers (ECUs) in the network. When functionally addressed messages are sent, the one to many communication between the client and the servers (ECUs) takes place. The server shall only respond to certain requests (further explained in response behaviour to functionally addressed request chapter.
NOTE: Some types of buses (e.g. LIN) might also support broadcast communication which is very similar to functionally addressed. The only difference is that a server response is never expected by the client during broadcast communication.
Response behaviour to functionally addressed request¶
Expected server behaviour in case of receiving functionally addressed request message with SubFunction parameter:
Client request |
Server capability |
Server response |
Comment |
||||
Addressing |
SPRMIB |
SID supported |
SF supported |
DataParam supported |
Message |
NRC |
|
functional |
False (bit = 0) |
YES |
YES |
At least 1 |
Positive Response |
— |
Server supports the requests and sends positive response. |
At least 1 |
Negative Response |
NRC = XX |
Server sends negative response because an error occurred processing the data parameters of request message. |
||||
None |
No Response |
— |
Server does not send a response. |
||||
NO |
— |
— |
— |
Server does not send a response. |
|||
YES |
NO |
— |
— |
Server does not send a response. |
|||
True (bit = 1) |
YES |
YES |
At least 1 |
No Response |
— |
Server does not send a response. |
|
At least 1 |
Negative Response |
NRC = XX |
Server sends negative response because an error occurred processing the data parameters of request message. |
||||
None |
No Response |
— |
Server does not send a response. |
||||
NO |
— |
— |
— |
Server does not send a response. |
|||
YES |
NO |
— |
— |
Server does not send a response. |
|||
Expected server behaviour in case of receiving functionally addressed request message without SubFunction parameter:
Client request |
Server capability |
Server response |
Comment |
||
Addressing |
SID supported |
DataParam supported |
Message |
NRC |
|
functional |
YES |
All |
Positive Response |
— |
Server supports the requests and sends positive response. |
At least 1 |
— |
Server supports the requests and sends positive response. |
|||
At least 1 |
Negative Response |
NRC = XX |
Server sends negative response because an error occurred processing the data parameters of request message. |
||
None |
No Response |
— |
Server does not send a response. |
||
NO |
— |
— |
Server does not send a response. |
||
- Where:
SPRMIB - flag informing whether Suppress Positive Response Message Indication Bit is set in the received request message
SID supported - flag informing whether Service Identifier in the received request message is supported by the server
SF supported - flag informing whether SubFunction in the received request message is supported by the server
DataParam supported - information whether values of data parameters (e.g. DIDs, RIDs, DTCStatusMask) in the received request message are supported by the server
NRC - Negative Response Code
XX - NRC code that is supported by the server and suitable to the current situation (e.g. NRC 0x21 busyRepeatRequest if server is currently overloaded and cannot process next request message)
Segmentation¶
If diagnostic message data to be transmitted does not fit into a single bus frame, then segmentation process is required to divide diagnostic message into smaller pieces called UDS Packets. Each UDS Packet (or N_PDU) fits into one frame. To visualize the concept, look on the figure below:
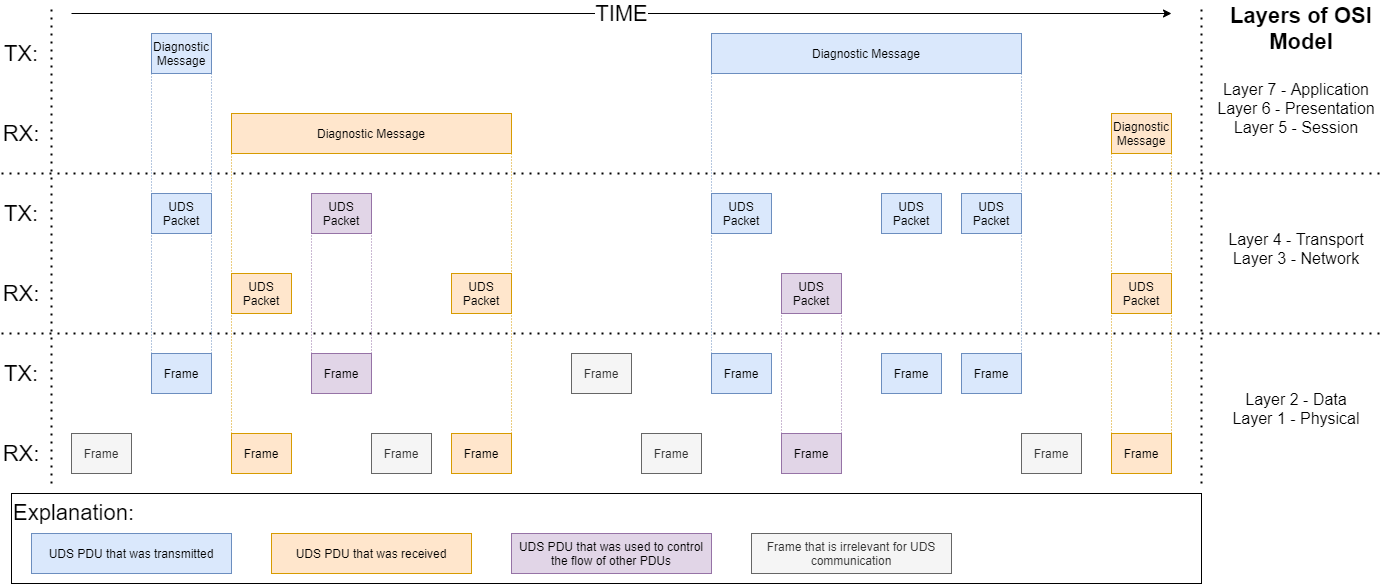
UDS Protocol Data Units on different layers of OSI Model.¶
- To summarize, we distinguish (in UDS package implementation) following entities that take part in UDS communication on different layers of UDS OSI Model:
Diagnostic message - also called ‘Application Protocol Data Unit’ (A_PDU)
UDS packet - also called ‘Network Protocol Data Unit’ (N_PDU). UDS packets types and transmission rules are bus specific and always fit into one frame.
Frame - the smallest piece of information exchanged by nodes in a bus network. Only specific frames take part in UDS communication.
Segmentation process is specific for a bus on which UDS Packets would transmitted.
UDS Packet¶
UDS packet is also called Network Protocol Data Unit (N_PDU). It is created during segmentation of a diagnostic message. Each diagnostic message consists of at least one N_PDU. There are some packets (N_PDUs) which does not carry any diagnostic message data as they are used to manage the flow of other packets (N_PDUs).
- UDS packet (N_PDU) consists of following fields:
Network Address Information (N_AI) - packet addressing
Network Protocol Control Information (N_PCI) - packet type
Network Data Field (N_Data) - packet date
Network Address Information¶
Network Address Information (N_AI) contains address information which identifies the recipient(s) and the sender between whom data exchange takes place. It also describes communication model (e.g. whether response is required) for the message.
Network Protocol Control Information¶
Network Protocol Control Information (N_PCI) identifies the type of UDS packet (Network Protocol Data Unit). Supported N_PCIs and theirs values interpretation are bus specific.
Network Data Field¶
Network Data Field (N_Data) carries diagnostic message data. It might be an entire diagnostic message data (if diagnostic message fits into one packet) or just a part (a single packet) of it (if segmentation had to be used to divide diagnostic message into smaller parts).